Chemical reactions are classified into two types based on energy transfer between the system and the surroundings. They are exothermic and endothermic reactions.
What Are Exothermic Reactions?
Exothermic reactions are chemical reactions that release energy in the form of heat or light (mostly heat energy is released). As the heat is released into the surroundings there will be an increase in the temperature of the system. Hence negative heat flow from the system to the surroundings will occur.
Exothermic reactions are spontaneous reactions and show higher randomness or entropy (ΔS>0) of the system. As the system releases energy to the surroundings, the enthalpy change of the reaction is a negative value. Exothermic reactions can be simply said by touching the wall of the container which feels warmer due to an increase in temperature by the release of heat.
Enthalpy (ΔH) is the sum of the internal energy of a system and the energy required to maintain the volume and pressure of that system. The enthalpy of products is lower than that of reactants because internal energy is released into the surroundings from the system. This can be explained by :
A + B → C + D
ΔH = {H products}-{H reactants}
ΔH = {HC+HD} – {HA+HB} = Positive value
Where,
ΔH = Enthalpy change the occurs after the reaction,
HC & HD = Enthalpies of product C & D respectively,
HA & HB = Enthalpies of reactants A & B respectively.
Examples: 1. Combustion of hydrocarbons
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(L) + Heat
2. Neutralization reaction
HCl (aq) + KOH (aq) → KCl (aq) + H20 (L) + Heat
What Are Endothermic Reactions?
Endothermic reactions are chemical reactions that absorb energy in the form of heat or light (mostly heat energy is absorbed). As the heat is absorbed from the surroundings there will be a decrease in the temperature of the system. Hence positive heat flow from the surrounding to the system will occur. These are non-spontaneous reactions.
As the system absorbs energy from the surroundings, the enthalpy change is a positive value. The enthalpy of the product is greater than that of the enthalpy of reactants because of the absorption of energy from the surroundings. This can be explained by the following:
A + B → C + D
ΔH = {H products} – {H reactants}
ΔH = {HC+HD} – {HA+HB} = Negative value
Where,
ΔH = Enthalpy change the occurs after the reaction,
HC&HD = Enthalpies of product C & D respectively
HA&HB = Enthalpies of reactants A & B respectively
Example: The instant cold packs contain ammonium nitrate and water. As we pop the pack, the water gets in contact with ammonium nitrate and by absorbing heat from surroundings the pack gets cool by the below reaction:
NH4NO3 (s) + H20 (L) → NH4+(aq) + NO3–(aq)
Other examples of endothermic reactions are:
- Evaporation of Liquid water from water vapor.
- Sublimation of solid carbon dioxide.
Energy Diagram of Exothermic Reactions and Endothermic Reactions
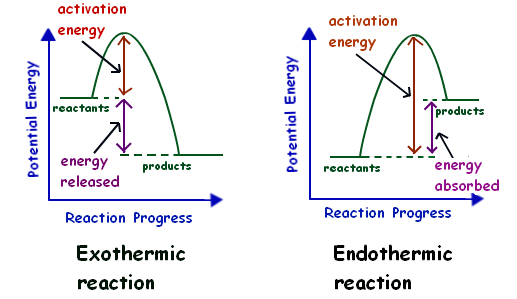

From the above diagram, the exothermic reactions show the potential energy of the product lower than that of the potential energy of the reactant whereas endothermic reactions show the potential energy of the product higher than that of the potential energy of the reactant.
Differences Between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
| Exothermic Reactions | Endothermic Reactions |
|---|---|
| Definition | |
| Chemical reactions which release energy in the form of heat or light are called exothermic reactions. | Chemical reactions which absorb energy in the form of heat or light are called endothermic reactions. |
| Energy | |
| Energy is released by the system. | Energy is absorbed by the system. |
| Spontaneity of reaction | |
| Exothermic reactions are spontaneous reactions. | Endothermic reactions are non-spontaneous reactions. |
| Change in enthalpy | |
| Change in enthalpy is negative in exothermic reactions. | Change in enthalpy is positive in endothermic reactions. |
| Potential energy | |
| Potential energy is higher in reactants than products. | Potential energy is lower in reactants than products. |
| Internal energy | |
| Internal energy is negative in exothermic reactions. | Internal energy is positive in endothermic reactions. |
| Temperature change | |
| An increase in temperature is observed in exothermic reactions. | A decrease in temperature is observed in endothermic reactions. |
| Examples | |
| Combustion of hydrocarbons, Neutralization reaction. | Evaporation of Liquid water to form water vapor, Sublimation of solid carbon dioxide. |
Conclusion
Both exothermic and endothermic reactions can be classified based on energy transfer between the system and surroundings. The main difference is that exothermic reactions release energy into the surroundings whereas an endothermic reaction absorbs energy from the surroundings.