In general, In between heat and temperature, we often get confused. It’s because if we look closely, they are very closely connected. Thus, the heat and the temperature difference. They can be interconnected, but they certainly aren’t the same.
It can give you a better understanding of how the world operates when you learn the difference between heat and temperature. The temperature will rise when we add heat to anything. Likewise, the heat will disappear if we decrease the temperature of anything. A closer look at both will help to better clarify the situation.
In this article, we will know the clear difference between Heat and Temperature
What is Heat?
Definition of Heat:
The extent to which a body or environment is hot or cold.
According to the meaning of heat, it is one of the essential energy for the survival of life on Earth. Heat transfer occurs from one body to another because of a temperature difference according to thermodynamics.
For various activities such as cooking, ironing, transport, etc, we use heat energy. In nature, this type of energy is also vital. Wind, rain, season changes, etc. depend on the gradient caused by uneven heating in different areas.
In accordance with the meaning of heat, energy from a warm to a cooler object is defined. The heat energy flow direction from the high-temperature to the low-temperature substance. This is because the molecules vibrate more quickly and vibrate less energy in the molecules. Also called heat content is vibrational energy. The body’s thermal content makes it warm or cold. The heat content is bigger, and the body is hotter.
Transfer of heat:
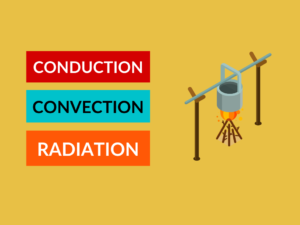
There are three mechanisms to transfer the heat are as follows:
Conduction:
This is the method by which the heat transfer takes place in direct contact between atoms and molecules.
Convection:
This is the method by which the movement of the heated substance leads to the transfer of heat.
Radiation:
It is the method by which electromagnetic waves transfer heat.
S.I unit:
Joule, calories.
Measuring device:
Calorimeter
What is Temperature?
“The body temperature is the degree to which the body is hot or cold.” Or “Proportional of the average kinetic energy. It feels hot or cold when we touch a body. The body’s temperature tells us how cold and hot a body is.
We say that two systems have the same temperature when in thermal balance. The temperature, on the other hand, is the property of a system equal to another when both systems are in thermal balance.
The energy of a thermodynamic system isn’t equivalent to the temperature; for example, the combustion temperature is much higher than an iceberg, but the heat energy in the whole iceberg is considerably higher than the energy in a match.
Temperature, similar to pressure or density, is referred to as an intense property, one that differs from the extensive characteristics such as mass, or volume, regardless of the quantity of matter.
There are two types of thermometers
That is as follows:
- Digital thermometer
- Analog thermometer
S.I unit:
Kelvin, Fahrenheit, celsius.
Temperature measurement:
Scale of Celsius (°C):
The freezing point (H2O) at O°C and the boiling point (H2O) at 100°C have this scale. The intermediate temperature is split into 100 units (degree).
The Celsius Scale disadvantages are:
Temperatures may be below O°C in some cases. Gas pressure and volume do not change in proportion to the temperature of Celsius.
The Scale of Kelvin (K):
This scale has absolute null as its scale has zero points. The grade means are identical to a degree of Celsius. The benefits are as follows:
On this scale, there are no bad temperatures.
In proportion to Kelvin, the pressures and volumes of all gases shall vary.
Absolute null is 273°C lower than O°C.
Measuring device:
Thermometer
Difference between Heat and temperature
In the below you will learn the clear difference between heat and temperature
| Heat | Temperature |
|---|---|
| 1. Definition | |
| Heat is the amount of energy in a body. | Temperature is the intensity of heat. |
| 2. Produce | |
| It produces a sensation of hotness | It is a measure of the degree of hotness or coldness |
| 3. Flow | |
| The flow of heat is higher to a lower temperature. | It is the condition that determines the direction of heat. |
| 4. Cause and effect | |
| Heat is a cause | Temperature is an effect. |
| 5. Units | |
| S.I unit - kcal, cal, joules | S.I unit - degree Celsius, Kelvin, Fahrenheit |
| 6. Exchange | |
| Heat is exchangeable and flows from one body to other | Temperature is not exchangeable and so cannot flow. |
| 7. Properties | |
| Not a property of a thermodynamic system. | Property of thermodynamic system. |
| 8. Energy | |
| The total amount of internal energy of a body. | Proportional of the average kinetic energy of molecules of a body |
| 9. Measuring device | |
| A measuring device is a calorimeter | A measuring device is a thermometer |
Bottom line:
As a result of the preceding discussion, the difference between heat and temperature is the energy transfer continues until the same temperature exists for the two bodies. Heat is called the form of energy that is transmitted from the warm body to a cold body. “Heat is the energy transferred by thermal contact between body and body because of the difference in temperature between body and body.”
Thus, heat is called transit energy. Once heat comes into the body, it is his inner energy and is no longer present in heat power.
Further related readings: