Difference Between PCOD and PCOS. Are PCOD and PCOS the same? Many women get confused between the 2, often using the 2 terms interchangeably, especially when trying to grasp the relation between PCOS, and PCOD. In reality, both the conditions are different, despite the similarities like being associated with the ovaries and causing hormonal disturbances.
Let’s take a more in-depth examine these two conditions and what makes them different from one another.
What is PCOD?
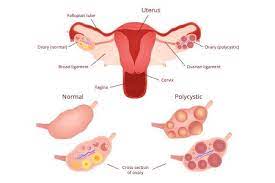
All women have two ovaries that release an egg alternately each month. The ovaries produce androgens or male hormones in minute quantities. PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease) may be a condition where the ovaries release plenty of immature or partially mature eggs which eventually grow to be cysts. A number of the common symptoms are abdominal weight gain, irregular periods, male pattern hair loss, and infertility. During this condition, the ovaries usually become enlarged and secrete large amounts of androgens that may cause havoc with a woman’s fertility and her body. The simplest treatment for PCOD often looks at reducing the severity of such symptoms.

What causes Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD)?
- Normally, the ovaries make female sex menhormones and a tiny amount of male sex hormones (androgens). These help regulate the normal development of eggs in the ovaries during each menstrual cycle.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome is related to an imbalance in these sex hormones. In PCOS, they start making slightly more androgens. This causes patients to stop ovulating, get pimples and grow extra facial and body hair.
- Follicles are sacs within the ovaries that contain eggs. Normally, one or more eggs are released during each menstrual cycle. This is called ovulation.
- In polycystic ovary syndrome, the eggs in these follicles do not mature and are not released from the ovaries. Instead, they can form very small cysts in the ovary, hence the name polycystic ovaries.
- PCOS seems to run in families, so the chance of having it is higher if other women in the family have PCOS, irregular periods, or diabetes
What is PCOS?
In women with PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome), the ovaries produce higher levels of androgen than usual, which interferes with the event and release of the eggs. A number of the eggs turn out to be cysts, which are small sacs crammed with liquid. Rather than being released during ovulation, these cysts build up within the ovaries and sometimes even get enlarged.
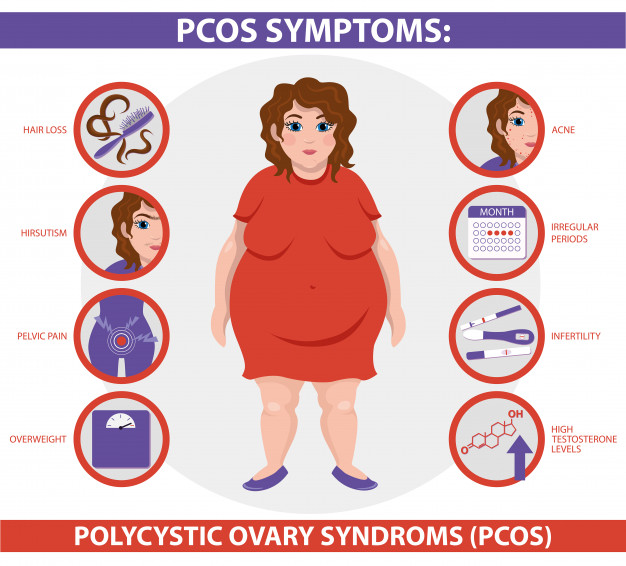

Common symptoms of PCOD/PCOS include:
- Acne
- Weight gain and trouble losing weight
- Extra hair on the face and body. Often women get thicker, darker facial hair and more hair on the chest, belly, and back.
- Thinning hair on the scalp
- Irregular periods. Often women with PCOS have fewer than nine periods a year. Some women have no periods others have very heavy bleeding
- Fertility problems. Many women who have PCOS have trouble getting pregnant (infertility)
- Depression
Investigations like blood sugar estimation, thyroid hormone tests, ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis are done. Sometimes serum androgens, luteinizing hormone and other hormone estimations may be ordered
Difference Between PCOD and PCOS
| PCOS | PCOD |
|---|---|
| Nature of the condition | |
| PCOS may be a serious condition.it can be a disorder | PCOD isn't considered to be truly a disease since with the proper diet and exercise, |
| Causative factors: | |
| Polycystic Ovary Syndrome may be a disorder of the endocrine system, | PCOD may be a condition developed by an imbalance of hormones. |
| Occurrence | |
| Polycystic Ovary Syndrome incorporates a lower number of patients. | PCOD is more common as compared. |
1. Causative factors:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome may be a disorder of the endocrine system, while PCOD may be a condition developed by the imbalance of hormones. It’s believed that hormonal imbalances and genetics play an important role in both conditions. The speculation is that prime levels of male hormones prevent ovaries from producing hormones and producing eggs normally. Insulin resistance and inflammation have also been linked to excess androgen production.
2. Occurrence:
PCOD is more common as compared. Almost one-third of girls around the globe suffer from Polycystic Ovarian Disease. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome incorporates a lower number of patients.
3. Impact of PCOD & PCOS on pregnancy:
Polycystic Ovarian Disease doesn’t lead to infertility in all women and shouldn’t be considered an obstacle towards pregnancy. In about 80 percent of cases, women can conceive with a little aid and experience a smooth pregnancy. For ladies with PCOS, conception will be a challenge because of hormonal irregularities. To conceive, one should have balanced hormonal cycles that may create an environment for the ovum to release and infuse with the sperm post-intercourse. Since the number of androgens in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is very high, the conception can become a bit of a challenge if one falls under the syndrome.
Maintaining a physiological state is crucial to stop still as treat hormonal disturbances and conditions. The simplest treatment for PCOD and PCOS will include timely diagnosis and also the appropriate steps that may help overcome the syndrome and make the journey towards conception successful.
Conclusion
Increased risk of endometrial cancer. Infertility (early treatment of polycystic ovary disease can help prevent infertility or increase the chance of having a healthy pregnancy). Obesity-related (BMI over 30 and waist circumference greater than 35) conditions, such as high blood pressure, heart problems, and diabetes. Possible increased risk of breast cancer


