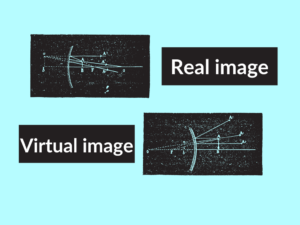
Real Image vs Virtual Image: Understanding the Differences
Introduction:
When discussing optics and imaging, two key terms that often arise are “real image” and “virtual image”. These terms refer to distinct types of images formed by the interaction of light with reflective or refractive surfaces. While both types of images have their own unique characteristics and applications, it is important to understand the differences between them. In this article, we will explore the concept of real and virtual images, provide examples of each, discuss their uses, and finally summarize the key differences between them.
What is a Real Image?
A real image is formed by the actual convergence of light rays. It can be captured on a screen or surface and is visible, similar to the image formed by a camera or projected onto a movie theater screen. Real images occur when light rays pass through a convex lens or converge after reflecting from a concave mirror.
Examples of Real Images:
- An image formed by a camera lens
- A projected image on a movie theater screen
- An image formed by a convex lens in a microscope
- An image formed by a concave mirror in a reflecting telescope
Uses of Real Images:
Real images have practical applications in various fields:
- Optical devices: Cameras, microscopes, telescopes
- Entertainment: Movie projectors, virtual reality systems
- Medical imaging: X-rays, CT scans, ultrasound
What is a Virtual Image?
A virtual image, on the other hand, is an optical phenomenon. It is formed by the apparent divergence of light rays and cannot be projected onto a screen or surface. Virtual images cannot be captured but are visible to the observer, similar to a mirror reflection. Virtual images are formed when light rays pass through a concave lens or diverge after reflecting from a convex mirror.
Examples of Virtual Images:
- The image seen in a plane mirror
- The image formed by a concave lens
- The image formed by a convex mirror in a rearview mirror
Uses of Virtual Images:
Virtual images are involved in various applications:
- Optical devices: Rearview mirrors, magnifying lenses
- Projection systems: Head-up displays, holographic displays
- Physics experiments: Virtual reality simulators
Differences between Real Image and Virtual Image:
| Difference Area | Real Image | Virtual Image |
|---|---|---|
| Formation | Formed by actual convergence of light rays | Formed by apparent divergence of light rays |
| Visibility on a Screen | Visible and can be projected onto a screen | Not visible on a screen or surface |
| Capture | Can be captured by a recording device | Cannot be captured |
| Image Orientation | Upright or inverted depending on the optical system | Always erect |
| Image Size | Can be magnified or reduced in size | Same size or larger than the object |
| Focus | In-focus or out-of-focus depending on the distance | Always appears to be in focus |
| Interaction with Light | Converges or converges and diverges | Diverges |
| Propagation | Can propagate and be projected onto a distant surface | Does not propagate and is limited to the observer’s vision |
| Position | Can be located in front of or behind the optical system | Always located behind the optical system |
| Nature | Physical representation of light rays | Imaginary representation of light rays |
Conclusion:
In summary, real images and virtual images are two distinct types of optical images formed by the interaction of light with reflective or refractive surfaces. Real images are formed by the convergence of light rays, can be projected onto a screen, and can be captured by recording devices. On the other hand, virtual images are formed by the divergence of light rays, cannot be projected onto a screen, and cannot be captured. The orientation, size, focus, and propagation characteristics also differ between the two types.
Knowledge Check:
- True or False: Real images can be captured by recording devices.
- True or False: Virtual images can be projected onto a screen or surface.
- Which type of image is formed by the convergence of light rays?
- Which type of image is formed by the divergence of light rays?
- Which type of image is always located behind the optical system?
- What is the primary use of real images in medical imaging?
- What type of mirror is involved in the formation of virtual images in a rearview mirror?
- What happens to a real image when it is located farther away from the optical system?
- What is the key difference between the formation of real and virtual images?
- Which type of image is always upright?
Answer: True
Answer: False
Answer: Real image
Answer: Virtual image
Answer: Virtual image
Answer: X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasound
Answer: Convex mirror
Answer: It becomes larger
Answer: The convergence and divergence of light rays
Answer: Real image
Related Topics:
- Optics: Refraction and Reflection
- Difference between Convex and Concave Lenses
- Mirror Image: Understanding Reflection