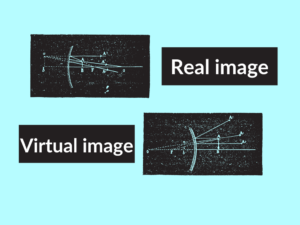
Difference Between Real and Virtual Images
Welcome to this comprehensive article that aims to explain the difference between real and virtual images. By understanding these concepts, you’ll gain insights into how these images work and their applications in various fields.
What are Real Images?
Real images are those formed when actual light rays converge or meet at a specific point. They can be projected onto a surface to create a visual representation of an object or scene. Real images are formed by convex lenses and concave mirrors.
Examples of Real Images:
- Photographic images captured by a camera
- An image formed on a cinema screen
- An image formed on the retina of our eyes
Uses of Real Images:
Real images have various applications in our daily lives and scientific fields:
- In photography for capturing moments and creating memories
- In cinematography for projecting movies onto screens
- In optical instruments like microscopes and telescopes for magnification
What are Virtual Images?
Virtual images are formed when light rays appear to diverge from a particular point, although they do not actually converge at that point. These images cannot be projected onto a surface, and they can only be seen through optical devices or mirrors.
Examples of Virtual Images:
- An image seen in a plane mirror
- An image formed by a concave lens
- An image seen in a rear-view mirror in a car
Uses of Virtual Images:
Virtual images find applications in various fields:
- In visual aids such as projectors, where the image is reflected onto a screen
- In rear-view mirrors to provide a wider field of view for drivers
- In educational demonstrations and experiments to visualize concepts
Differences Between Real and Virtual Images
| Difference Area | Real Image | Virtual Image |
|---|---|---|
| Formation | Real images are formed by the convergence of light rays. | Virtual images are formed by the apparent divergence of light rays. |
| Projection | Real images can be projected onto a screen or surface. | Virtual images cannot be projected or captured on a screen. |
| Nature | Real images are on the same side as the object. | Virtual images are on the opposite side of the object. |
| Visibility | Real images are visible and can be seen directly. | Virtual images are not visible but can be seen indirectly. |
| Size | Real images can be magnified or reduced in size. | Virtual images are generally the same size as the object. |
| Interaction | Real images can interact with other objects or screens. | Virtual images do not interact with other objects or screens. |
| Formation Lens/Mirror | Real images can be formed by convex lenses and concave mirrors. | Virtual images can be formed by concave lenses and plane mirrors. |
| Light rays | Real images converge light rays to a point or location. | Virtual images appear to diverge light rays from a point or location. |
| Applications | Real images are used in photography, cinema, and optical instruments. | Virtual images find applications in visual aids, rear-view mirrors, and educational demonstrations. |
Conclusion:
To summarize, real images are formed by the convergence of light rays and can be projected onto a surface, while virtual images are formed by the apparent divergence of light rays and cannot be projected but can only be seen indirectly. Understanding the differences between real and virtual images helps in various scientific and practical applications.
People Also Ask:
- Q: Can real and virtual images be seen by the naked eye?
A: Real images can be seen directly with the naked eye, while virtual images can only be seen indirectly through optical devices or mirrors. - Q: Are real images always upright?
A: Real images can be inverted or upright, depending on the optical system creating them. - Q: Are virtual images smaller than the object?
A: Virtual images are generally the same size as the object, although they can be magnified or reduced in size using optical devices. - Q: Can virtual images be photographed?
A: Virtual images cannot be captured directly by a camera as they do not physically exist; however, they can be captured indirectly by photographing the optical device or mirror creating the image. - Q: How are real and virtual images used in medical imaging?
A: Real images are used in medical imaging techniques like X-rays and ultrasound to produce detailed visuals of the internal structures, while virtual images are used in techniques like MRI and CT scans to create 3D representations of the body.